Vibrations are one of the most important factors that affect the operation and lifetime of electrical rotating machines. Permanent monitoring and periodic vibration tests provide insight into the dynamic state of the machine and can indicate problems during machine exploitation. With hydro generators, for example, radial vibrations are mainly monitored and analyzed and these vibrations also comply with standards and contractual/tender requirements which define criteria of reliability for generator in operation. In addition to radial or flexural vibrations, problems and failures of rotating machines can also be caused by the occurrence of torsional vibrations, which can lead to major machine damage and thus financial losses.
We recently developed Shaft Torque and Power Measurement (STP) system for measurement and analysis of torsional vibrations. The system expands the picture of the dynamic behavior of rotating machines, contributes to monitoring of machine health and to early detection of possible failures and problems.
Torsional vibrations
The occurrence of torsional vibrations can be expected, in some extent, with all rotating machines during operation. Not enough attention is given to torsional vibrations, especially concerning the design and permanent monitoring of the hydro-generator rotor. The research shows the extensive damage that occurs on rotating machines because of the fatigue caused by shaft torsional loads.
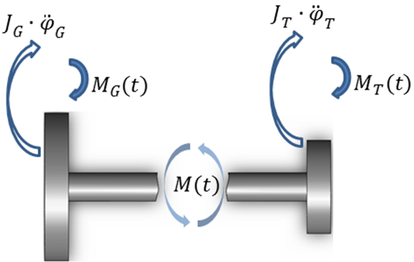
Fig 1. Simplified torsional dynamic model of the rotor
The most important parts of the model are generator rotor (G) and the turbine runner (T). Shaft twisting (torsion) occurs exactly between these two masses. In rated operation, we can say that the torsional torque affecting the shaft/s is balanced with a magnetic moment in the air gap between the stator and rotor if we ignore the friction losses in the bearings. Thus, the drive torque is balanced with load torque. While these two moments are equal in amount and opposite in sign, the rotational speed is constant and the shaft will be twisted for a constant deflection. This rated torque represents the static load and does not cause shaft vibrations. Vibrations can be encouraged by some kind of disturbance force either on turbine runner or generator rotor. Any change of the drive or load torque, periodic or pulse, will cause a change of the shaft angle and thus the occurrence of forced torsional vibrations.
Transient phenomena that disrupt the stability of the rotor system most commonly are a result of errors in synchronization, power oscillation or sudden electrical disturbance in the network, as well as possible generator short circuit. These phenomena cause an increase in torsional loads and torsional vibrations.
The increase of torsional vibrations can be also caused by the sudden changes in the network load. The duration of such sudden changes in the network can last from a few seconds to several minutes, which also influences the final effects of changes on the system stability. Often these transient events do not induce torsional resonance of the shaft to a greater degree, but sometimes the characteristics of transient waveform match torsional resonance, resulting in a number of cycles of severe stress. Accumulation of more cycles can lead to problems and failures due to vibration fatigue, but also to the creation or expansion of any cracks on the shaft.
System development and design
Torsional vibrations usually have greater importance in the design and dimensioning of turbo generators and ship engines, but they are also an important factor in the design of hydro generators. These vibrations of the rotor system are seldom analyzed – mainly during commissioning, usually using gage measurements of the shaft angle.
STP system is based on a multi-channel processing unit with a real-time controller. The processing unit is combined with input and output analog and digital modules, and it is based on fast and reliable industrial PLC, designed for harsh conditions and environments with all necessary certificates and references for use with electrical machines. It has a wide measuring range and very low measuring error.
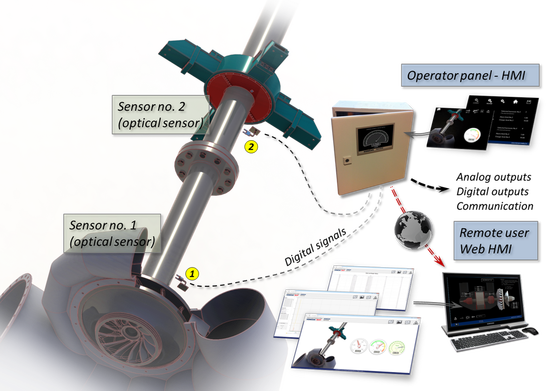
Fig 2. System for shaft torsion measurement
With its configuration STP system allows continuous monitoring of the shaft torsion during all machine states. At the same time, it compares and analyses the results obtained with other machine parameters such as engine speed, power, voltage and current of all phases and excitation voltage. With detailed analysis, comparisons and monitoring of trends it can be determined which conditions are less favorable for the machine, how often these conditions occur and how they affect other parameters of the machine.
The resulting data can be compared with the vibrational state of the machine obtained by measuring radial vibrations. This can further be used to bring conclusions to the impact of unfavorable working conditions and on the impact of shaft torsional vibrations to the increase of other vibration parameters, which may lead to material damage of complex mechanical system components.
Conclusion
Due to a relatively long period that passes from the onset of expressed torsional vibrations to occurrence of major damage, there is a possibility to timely detect and prevent faults by using the system for continuous measurement and analysis of shaft torsional vibrations.
Although the impact of power oscillation and other disturbances in power network to the generator lifetime is often ignored, installation of permanent monitoring of torsional vibrations increases the reliability of rotating machines. By measuring and analyzing torsional vibrations with STP system and in combination with other important measurements on the machine, excitation dynamic torque on the turbine can be determined, which is relevant for the lifetime of the generator rotor.
Since most of the turbo and hydro generators have radial vibration monitoring installed, by installing the STP system dynamic behavior of the machine can be further complemented. In particular cases, only measurement and data analysis can distinguish the impact of possible superposition of flexural and torsional vibrations, which further confirms the importance of rotor vibration measurement.